Storage Statistics
Analyze storage usage and costs at dataset, table, and column level.
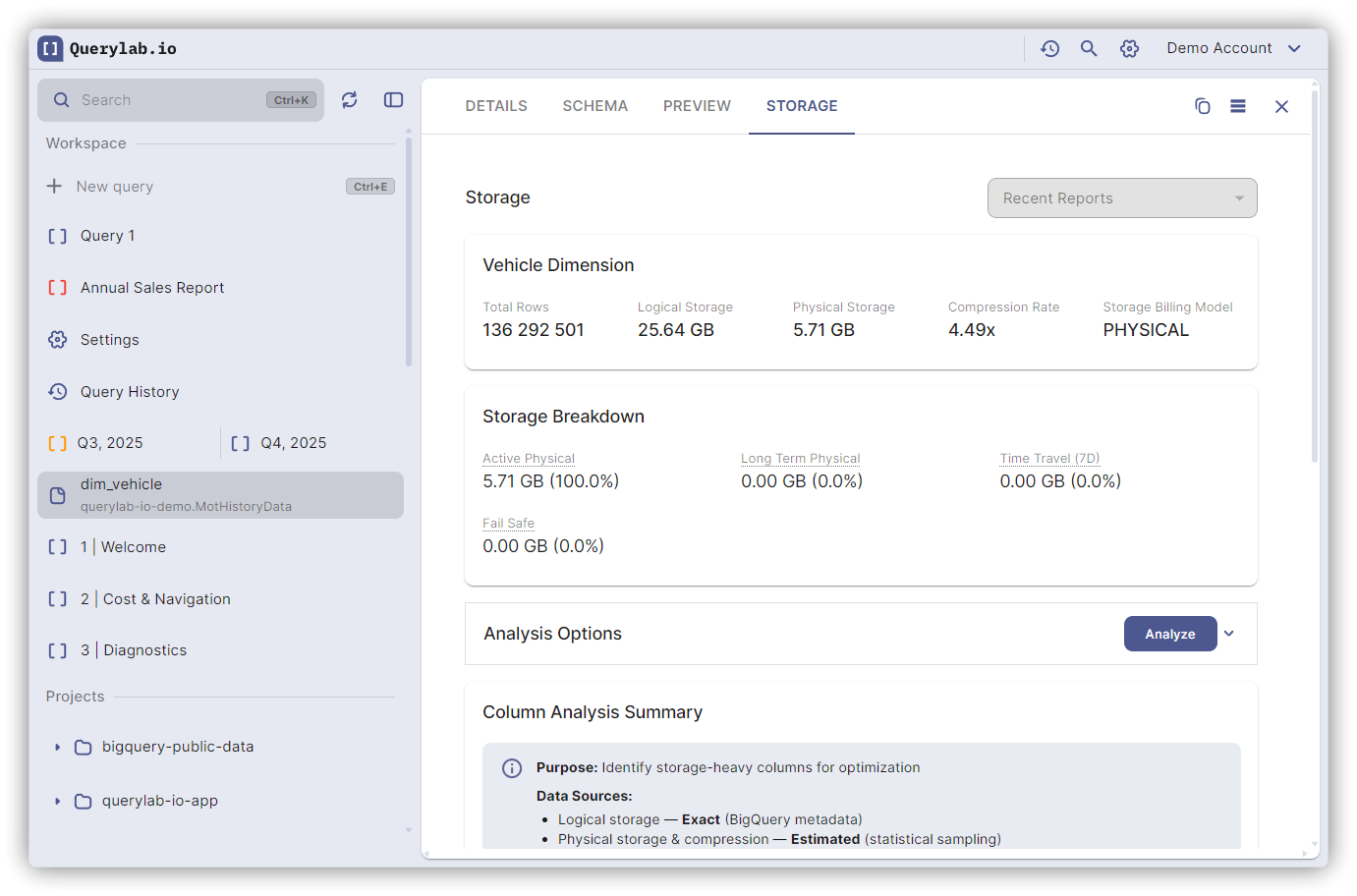
Dataset Storage
Hover over dataset in Schema Browser → Click Actions button (⋮) → "View Storage Stats"
Shows:
- Total size (logical bytes)
- Number of tables
- Partitioned vs non-partitioned breakdown
- Cost comparison: Logical vs Physical billing
Table Storage
Hover over table → Click Actions button (⋮) → "Storage Statistics"
Overview Metrics
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Logical Bytes | Uncompressed size (logical billing basis) |
| Physical Bytes | Actual compressed storage |
| Time Travel Bytes | Storage for 7-day history |
| Compression Ratio | Physical / Logical (lower = better compression) |
Column-Level Analysis
Detailed per-column breakdown:
- Storage size - Logical and physical GB per column
- Compression ratio - How well each column compresses
- % of table - Column's share of total storage
- NULL % - Percentage of NULL values
- Cost impact - Per-column cost under each billing model
Billing Model Comparison
| Model | What's Charged |
|---|---|
| Logical | Active + Long-term storage (time-travel FREE) |
| Physical | Active + Long-term + time-travel + fail-safe |
The analyzer recommends which billing model saves you money.
Adaptive Sampling
For large tables, Querylab.io uses intelligent sampling:
Quality Presets:
- Fast: Quick estimates, lower precision
- Balanced: Good accuracy, reasonable time
- Accurate: High precision, longer analysis
Each column converges independently - analysis stops when confidence is high enough.
Optimization Recommendations
The analyzer identifies:
- GUID columns - Suggests FARM_FINGERPRINT or BYTES alternatives
- Sparse columns - Flags columns with >95% NULLs
- Low compression - Highlights inefficient column types
- Potential savings - Calculates cost reduction from optimizations
Storage Cost
BigQuery storage pricing:
- Active storage: ~$0.02/GB/month
- Long-term storage: ~$0.01/GB/month (tables not modified 90+ days)
Actual pricing varies by region.
Tips
- Drop unused tables
- Set expiration on temporary tables
- Use partitioning to enable partition pruning
- Consider BYTES for UUID columns (4x smaller than STRING)
- Review sparse columns for potential removal